Patients often say “nothing was hurting until now”. There are several causes of pain. The main sites of pain are from the nerve, the gums, muscles or jaw joints. The fact is most decay in teeth, cracked teeth or gum problems usually have started months earlier. When you have pain it can mean permanent damage to the nerve of the tooth or permanent loss of bone. For the purposes of this article, we’ll focus on decay of teeth.
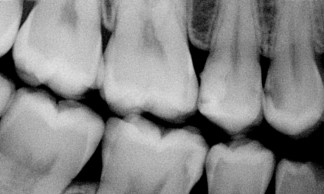
Most of the time, you may not notice the early stages of decay. However there are often tell-tale signs of a problem. These include food getting caught between the teeth; or sensitivity to cold, hot, or biting. Sometimes there are no symptoms at all. During a routine check-up, x-rays, called bitewings, are taken to assess for decay in the teeth. Often decay can be found half way to the nerve with no symptoms reported by the patient.
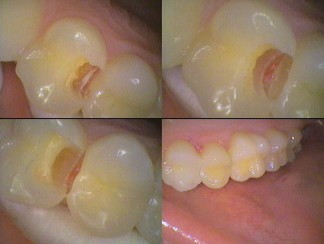
The problem is that the larger the decay, the weaker the tooth is for life! Fillings are a poor second to your own tooth structure. A digital x-ray does not tell you if the nerve is able to cope with the decay and then the filling as well. The dentist can’t leave the decay as it will worsen so a filling is done. The nerve may still die despite all our best efforts. However, the success of a nerve coping with a deep decay and then a deep filling, is greater if there have been little symptoms. It’s better we let you know there is a problem than for you to tell us! The earlier decay is picked up, the more options you have for life. Additionally, the cost is greatly reduced and long term complications can be avoided. If detected even earlier as a white spot lesion, treatment of early decay procedures can used to avoid drilling.
If the nerve does die and there is sufficient tooth structure, then root canal treatment can be done. Otherwise extraction of the tooth is the final option. So not having any pain does not mean that there is nothing wrong. You can make sure there is nothing wrong with regular examinations and x-rays.
How often do we take bitewing x-rays? It depends on the person risk profile. It can range from every 12 months for high risk to 3 years for low risk.
 479 Marrickville Road
479 Marrickville Road