Treatment of Enamel defects (Hypoplasia and Hypo-calcification) – Part Three: Restoration
These enamel defects leave a porous, soft, NON-wear resistant, stained and a NON decay resistant structure. They need constant monitoring and, if necessary, early intervention should be carried out.
However, if the diet is not controlled, or is the enamel is worn away, bacteria can invade the next layer of the tooth, the dentine. This causes decay to occur. We need to remove the decay and place a filling. This is to prevent the decay destroying the tooth. In this type of porous enamel decay can progress quickly.
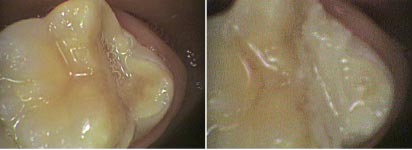
Sometimes decay does not occur but the exposed dentine is sensitive or forms a crater that allows food to wear further loss of dentine and enamel. A filling is needed in this situation to protect the dentine and build up the shape of the worn tooth.
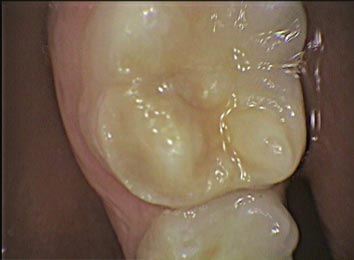
However, as the enamel is porous the bond or seal of the filling to the tooth is compromised. Good enamel is like a crystal and chemical process bonding is designed for this type of enamel. Porous enamel is, well porous/chalky, and a poor bond and may leak.
This means constant checks of the filling are needed and any change in sensitivity should not be ignored.
Need an Appointment?
If you’d like to book an appointment with the dentist at Seymour Dental then call us in Dulwich Hill, Sydney on (02) 9564 2397 or
contact us
Next week
Treatment of Enamel defects (Hypoplasia and Hypo-calcification) - Part Four: More extensive treatment - Crowns